Last updated: 2 Jul 2024 | 13706 Views |

Ganoderma (灵芝) is the dried sporophore of Ganoderma lucidum (Leyss. ex Fr.) Karst. or G. sinense Zhao, Hsu et Zhang, family Polyporaceae.
Other name
Lin-Zhi (Thai name), Lingzhi (Chinese name), Glossy Ganoderma
Macroscopic character
Chizhi (G. lucidum): Outline umbrella-like, pileus reniform, semi-rounded or subrounded. Shell hard, yellowish-brown to reddish-brown, lustrous, with circular arise stripe and radiate wrinkle, edge thin and even, frequently incurved slightly. The lower part white to pale brown. Stipe cylinder, laterally grown, few leaning grown , reddish-brown to purplish brown, luminous. Spore small and fine, yellowish-brown. Odor, slightly aromatic, taste, bitter and astringent.

Zizhi (G. sinense): Shell purplish-black, with lacquer-like lustre. The lower part rusty-brown. Stipe longer than Chizhi.
Cultivated Ganoderma: Sporophore relatively sturdy, plump. Shell frequently coated with a large of yellowish-brown powder-like spores.
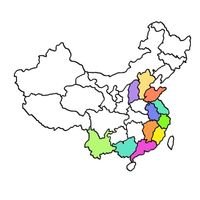
Important cultivation area
East and Southwest of China, Hebei, Shanxi, Jiangxi and Guangxi provinces.
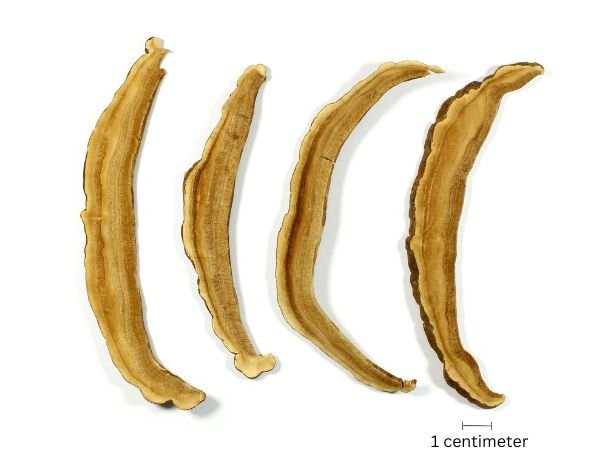
Processing method
Eliminate foreign matters, cut into thick slice, and dried in the shade or oven at 40-50°.

Traditional Chinese Medicine action
Sweet; neutral. Enter heart, lung, liver and kidney channels. Tonify qi, transquilize mind, suppress cough, and relieve wheezing.
Usage and dosage
6-12 g, decoction for oral use.
* Contraindication and precaution *
-
Copy right of Huachiew Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinic.
For public knowledge.
Commercially copy without permission is prohibited.
19 Feb 2024
23 Apr 2024